로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임, 차이브, 딜 추출물의 항산화 및 항균효과
Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Effect of Rosemary, Parsley, Thyme, Chive, and Dill Extracts
迷迭香、欧芹、百里香、细香葱和莳萝提取物的抗氧化和抗菌作用
Article information
Abstract
목적
로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임, 차이브, 딜 추출물의 항산화 및 피부와 관련 균에 대한 항균효과를 평가하여 천연 항균제 및 향장품 소재로서의 가능성을 확인하고자 한다.
방법
5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임, 차이브, 딜)을 70% 주정에탄올로 추출하여 시료로 사용하였다. 항산화 효과는 총 폴리페놀과 총 플라보노이드 함량, DPPH 라디컬, ABTS 라디컬 소거능, SOD 유사활성능을 측정하였다. 그리고 피부와 관련된 Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, Corynebacterium xerosis, Malassezea furfur, Trichophyton mentagrophytes에 대해 paper disc법을 사용하여 항균효과를 측정하였다.
결과
로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임, 차이브, 딜 에탄올 추출물 중 총 폴리페놀과 플라보노이드 함량은 로즈마리와 파슬리 추출물이 높은 함량이 확인되었으며, DPPH, ABTS 라디컬 소거능, SOD 유사활성은 로즈마리>파슬리>타임>차이브>딜 순으로 확인되었다. 항균효과를 측정한 결과 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물5 mg/mL의 농도에서 S. epidermidis는 로즈마리=파슬리=타임>차이브=딜 순으로 확인 되었으며, P. acnes는 로즈마리>파슬리>딜>타임=차이브 순으로 확인 되었다. C. xerosis는 로즈마리>파슬리>딜>타임=차이브 순으로, M. furfur는 로즈마리>파슬리> 딜>차이브>타임 순으로, T. mentagrophytesn는 로즈마리>파슬리>차이브>딜>타임 순으로 항균효과가 확인되었다.
결론
로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임, 차이브, 딜 에탄올 추출물은 항산화 및 항균효과가 확인되어 천연항균제 및 향장품 소재로서의 가능성이 확인되었다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to confirm the potential of rosemary, parsley, thyme, chive, and dill extracts as natural antimicrobial agents and incense cosmetic materials by evaluating the antioxidation effects and antimicrobial effects on the skin and related microorganisms.
Methods
Rosemary, parsley, thyme, chive, and dill were extracted with 70% ethanol and used as a sample. Antioxidant effects were measured at the total polyphenol and flavonoid content, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical, 2,2'-azinobis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) radical scavenging effects and superoxide dismutase (SOD)-like activity effect. And for Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, Corynebacterium xerosis, Malassezia furfur, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes related to the skin, the antimicrobial effect was measured using the paper disc method.
Results
Among the rosemary, parsley, thyme, chive, and dill extracts, the total polyphenol and flavonoids were found to be high in rosemary and parsley extracts. DPPH and ABS radical scavenging effects and SOD-like activity effects were confirmed to be in the order of rosemary>parsley>thyme> chives>dill. As a result of measuring the antimicrobial effects at a concentration of 5 mg/mL, S. epidermidis was confirmed to be in the order of parsley=rosemary=thyme>chive=dill, P. acnes was confirmed to be in the order of rosemary>parsley>dill>thyme=chive, C. xerosis was confirmed to be in the order of rosemary>parsley>dill>thyme=chives, M. furfur was confirmed to be in the order of rosemary>parsley>dill>chives>thyme, and T. mentagrophytes was confirmed to be in the order of rosemary>parsley>chives>dill>thyme.
Conclusion
Rosemary, parsley, thyme, chive, and dill extracts were confirmed to have antioxidant and antimicrobial effects, confirming their potential as natural antimicrobial agents and incense cosmetic materials.
Trans Abstract
目的
评估迷迭香、欧芹、百里香、细香葱和莳萝提取物对皮肤和相关细菌的抗氧化和抗菌作用,以确认它们作为天然抗菌剂和化妆品材料的潜力。
方法
通过测定总多酚和总黄酮含量、DPPH自由基清除活性、ABTS自由基清除活性和SOD样活性确定其抗氧化作用。并采用纸盘法对皮肤相关的表皮葡萄球菌、痤疮丙酸杆菌、干燥棒杆菌、糠秕马拉色菌和须癣毛癣菌进行抗菌效果测定。
结果
在迷迭香、欧芹、百里香、细香葱和莳萝提取物中,发现迷迭香和欧芹提取物中的总多酚和类黄酮含量很高。DPPH和ABS自由基清除作用和SOD样活性作用被证实为迷迭香>欧芹>百里香>细香葱>莳萝。在浓度为5 mg/mL时,对表皮葡萄球菌的抗菌效果顺序为欧芹=迷迭香=百里香>细香葱=莳萝;对痤疮丙酸杆菌抗菌效果顺序为迷迭香>欧芹>莳萝>百里香=细香葱,对干燥衣原体的抗菌效果顺序为迷迭香>欧芹>莳萝>百里香=细香葱;对马拉色菌的抗菌效果顺序为迷迭香>欧芹>莳萝>细香葱>百里香;对须癣毛癣菌的抗菌效果顺序迷迭香>欧芹>香葱>莳萝>百里香。
结论
迷迭香、欧芹、百里香、细香葱和莳萝提取物被证实具有抗氧化和抗菌作用,证实了它们作为天然抗菌剂和熏香化妆品材料的潜力。
Introduction
현대인의 생활수준의 향상과 인간의 평균 수명이 증가하면서 건강한 삶과 외적인 미에 대한 욕구가 강해지고, 건강과 웰빙에 대한 인식이 증가하여 노화 억제에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있다(Nam & Ko, 2020).
인체의 피부는 보호적 기능 외에 다양한 상재균을 갖고 있으며, 화학적 자극제, 환경오염 및 자외선과 같은 피부의 자극에 노출되면 활성산소를 증가시켜 피부의 면역 기능 저하, 염증성 알레르기 질환인 여드름, 아토피성 피부염 유발 및 기미, 주름, 탄력 감소 등의 각종 기능 저하로 인한 노화가 촉진된다(Ko et al., 2020; Park & Park, 2020).
이러한 변화에 따라 기능성 화장품 시장이 증가하기 시작했으며, 특히 화장품 원료의 안전성과 새로운 원료의 기능성에 대한 관심과 연구가 증가하기 시작했다(Cho et al., 2022).
화장품 산업은 일부 피부자극을 유발하는 유기합성 성분이 사용되고 있으며, 피부 트러블에 대한 소비자들의 불만이 늘어나면서 화장품의 추세는 친환경, 천연성분, 저자극 화장품의 개발이 활발히 증가하고 있다(Kim & Leem, 2020; Yoo & Lee, 2020).
항산화능은 자유 라디컬을 제거하는 작용을 의미한다. 모든 세포는 에너지의 생성 과정에서 활성산소를 생성하며, 만들어진 자유 라디컬은 면역반응, 세포 분화 조절, 대사 물질 합성 등 세포에 필수적인 작용에 사용된다. 하지만 염증반응이나 과도한 자외선 노출에 의해 과 생성된 자유 라디컬은 면역 질환, 암, 세포 노화 등 부정적 영향을 준다(Kim, 2021). 항산화제로는 합성 항산화제가 경제적으로 유리하여 많이 이용되었지만 여러 가지 부작용이 지적되면서 합성 항산화제 대신(Ji et al., 2021) 자연주의 바람과 함께 화장품의 사용목적이 피부미화, 청결뿐만 아니라 건강과 웰빙, 질병치유, 노화예방 개념으로 항산화, 항노화, 항주름, 미백 등 다양한 생리활성 기능을 지닌 추출물들을 많이 선호하게 되었다(Lee et al., 2021).
따라서 화장품의 천연자원 유래의 생리활성 물질에 대한 관심이 높아지며, 연구와 개발이 활발하게 진행되고 있다(Lee & Kang, 2021).
우리 생활에 널리 이용되고 있는 허브(Herb)는 라틴어의 herba에서 비롯된 '풀'이라는 뜻이지만 향기와 풍미가 독특하고 저마다 각기 다른 향과 효능을 가지고 있으며, 줄기, 잎, 꽃, 뿌리 등의 부위가 인간에게 유용하게 이용되는 식물의 총칭으로 쓰이고 있다(Park et al., 2012). 허브는 오랫동안 식용 향신료와 약용으로 사용되어 왔으며, 항균, 항산화, 항염증 등의 생리활성을 갖는 성분을 많이 함유하고 있어, 건강기능식품, 화장품 등의 제품이 증가하고 있으며, 지속적으로 연구되고 있다(Park et al., 2020).
본 연구에서는 로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜 추출물의 항산화 효과를 확인하기 위해 총 폴리페놀과 총 플라보노이드 함량, DPPH 라디컬 소거능, ABTS 라디컬 소거능, SOD 유사활성을 측정하였으며, 피부와 관련된 여드름 원인균, 비듬 원인균, 무좀과 백선증을 유발하는 원인균에 대해 항균효과를 측정하여 기능성 천연 항균제 및 향장제품 소재로서 개발 가능성을 알아보았다.
Method
1. 실험재료 및 추출방법
본 연구에 사용된 실험재료는 5종의 허브는 로즈마리(Rosemary, Salvia rosmarinus), 파슬리(Parsley, Petroselinum crispum), 차이브(Chives, Allium Schoenoprasum), 타임(Thyme, Thymus vulgaris), 딜(Dill, Anethum graveolens)은 국내 허브 농장에서 구입하여 실험에 사용하였다.
재료 추출방법은 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜)을 각각 100 g에 70% 주정 에탄올을 1 L을 넣고 60℃에서 24 h 침지 추출하였다. 추출액을 여과(Whatman filter paper No.1; GE Healthcare, Belgium)한 후에 회전식 감압농축기(EYELA N-1000; Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Japan)로 농축한 후, 동결건조기(PVTFA 10AT; ILSIN, Korea)에 72 h 동안 동결 건조하여 실험을 진행하였다.
2. 실험 방법
가. 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜) 에탄올 추출물의 항산화 효과 측정
1) 총 폴리페놀 함량 측정
5 종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 총 폴리페놀 함량은 Folin & Denis 방법에 따라 측정하였다(Folin & Denis, 1915). 1 mg/mL로 희석한 추출물 50 μL에 정제수 650 μL를 넣고 Folin-Denis reagent를 50 μL을 가하여 3 min 동안 실온에서 반응시킨 후 10% sodium carbonate (Na2CO3; Sigma-Aldrich, USA)을 100 μL 첨가하고 후 정제수 150 μL 넣어 혼합하여 37℃에 1 h 반응시킨 후 725 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 폴리페놀 함량은 tannic acid (Sigma-Aldrich)를 표준물질로 한 표준곡선을 통해 함량을 구하였다.
2) 총 플라보노이드 함량 분석
총 플라보노이드 함량은 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물(1 mg/mL) 100 μL에 1 mL diethylene glycol (Sigma-Aldrich)을 첨가하고, 다시 1 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH; Sigma-Aldrich) 100 μL 넣어 잘 혼합시켜 37℃ water bath에 1시간 반응시킨 후 UV-Vis spectrophotometer를 이용하여 420 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 표준곡선은 naringin (Sigma-Aldrich)의 농도를 0-300 μg/mL가 되도록 하고 이로부터 총 플라보노이드 함량을 구하였다.
3) DPPH 라디컬 소거능 측정
DPPH (Sigma-Aldrich) radical을 이용한 항산화 활성은 Blois (1958)의 방법을 변형하여 사용하였다. 1 mM DPPH 용액 100 μL와 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물을 100 μL씩 취하여 혼합한 후 30 min 암 상태에서 방치한 후 잔존 radical 농도를 ELISA reader를 이용하여 517 nm에서 측정하였다. 활성비교를 위하여 항산화 물질로 잘 알려진 ascorbic acid (vitamin C; Sigma-Aldrich)와 butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT; Sigma-Aldrich)비교하였다.
4) ABTS radical 소거능 측정
5 종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 ABTS 소거능은 Re et al. (1999)의 방법으로 측정하였다. 시험 용액은 증류수에 7 mM ABTS와 2.45 mM potassium persulfate를 첨가하여 상온에서 16시간 배양하여 ABTS 양이온을 생성시킨 후 734 nm에서 흡광도의 값이 0.7 이하가 되도록 희석하여 제조하였다. 그 다음 ABTS 용액 100 μL에 추출물 100 μL을 가한 후 6 min 후에 734 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 음성대조군(2.45 mM potassium persulfate buffer)의 흡광도와 비교하여 흡광도를 감소시키는 정도를 %로 나타내었다. 활성비교를 위하여 항산화 물질로 잘 알려진 vitamin C, BHT와 비교하였다.
5) SOD 유사활성 측정
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 SOD 유사활성 측정은 Marklund & Marklund (1974)의 방법에 따라 시행하였다. 추출물 0.2 mL에 pH 8.5로 보정한 tris-HCl buffer 3 mL와 7.2 mM pyrogallol 0.2 mL를 넣어 혼합한 후, 35℃에서 10 min간 반응시킨 후 1 N HCl로 반응을 정지시킨 다음 420 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 활성비교를 위하여 항산화 물질로 잘 알려진 vitamin C, BHT와 비교하였다.
나. 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜) 에탄올 추출물의 항균효과 측정
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 항균효과 측정에 사용한 균주는 한국생명공학연구원 생물자원센터에서 분양 받았다. 피부상재균인 Staphylococcus epidermidis, 여드름 원인균인 Propionibacterium acnes, 액취의 원인균인 Corynebacterium xerosis, 비듬의 원인균인 Malassezea furfur, 무좀의 원인균인 Trichophyton mentagrophytes를 사용하였다. 5 종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 항균효과는 paper disc법을 사용하였다(Davidson & Parish, 1989). 시험 균 농도는 650 nm에서 optical density (O.D)값이 0.4 (106 CFU/mL)가 되게 한 후 0.7% 한천이 첨가된 배지에 잘 혼합한 다음 고체배지 위에 분주하여 균 접종 배지를 만들었다. 고체배지 위에 멸균된 8 mm paper disc를 올려 놓은 후 0.25-5 mg/mL가 되도록 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물을 흡수시킨 다음 24-37℃에서 24 h 동안 배양 후 disc 주위의 clear zone을 측정하였으며, DMSO 20 μL을 함유한 disc를 대조군으로 측정하였다. Clear zone은 paper disc의 직경을 포함하지 않았다.
3. 통계
실험결과는 평균±표준편차 또는 표준오차로 나타내었으며, 통계학적 유의성 검정은 student's t-test로 검정하였으며, p-value가 0.05 이하 일 경우 유의성을 인정하였다. 통계처리는 SPSS 12.0 K for Windows (Release12.0.1; SPSS Inc., USA)를 사용하였다.
Results and Discussion
1. 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜) 에탄올 추출물의 항산화 효과
가. 총 폴리페놀과 플라보노이드 함량
페놀 화합물은 식물계에 널리 분포되어 있는 2차 대사산물로 다양한 구조와 분자량을 가진다. 또한 phenolic hydroxy기를 가지고 있어 단백질과 같은 큰 분자들과 결합하는 성질이 있으며, 항산화 효능의 생리활성 가능을 가지고 있다(Lee & Kim, 2020a).
총 폴리페놀 함량은 Folin-Ciocalteu reagent가 추출물의 폴리페놀성 화합물에 의해 환원된 결과, 몰리브덴 청색으로 발색하는 것을 원리로(Lee, 2017) 분석한 결과, 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물 1 mg/mL에 포함되어 있는 총 폴리페놀의 함량은 Table 1과 같다.
로즈마리(149.73 μg/mL)>파슬리(131.89 μg/mL)>타임(106.12 μg/mL)>차이브(33.40 μg/mL)>딜(32.20 μg/mL) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 확인되어 로즈마리 추출물이 가장 높은 함량이 확인되었다.
플라보노이드는 C6-C3-C6의 구조를 갖는 화합물로서 식물의 꽃, 줄기 및 열매 등에 많이 함유되어 있으며, 항산화, 항염증 효과, 면역개선, 항바이러스 등 여러 생리활성 작용이 있어(Park & Na, 2020), 혈관개선 및 항산화 작용 등에 피부노화 방지효과 등도 보고되고 있다(Park & Kang, 2020).
Diethyline glycol 비색법에 의한 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물 1 mg/mL에 포함되어 있는 총 플라보노이드 함량은 Table 1과 같이 파슬리(96.46 μg/mL)>로즈마리(93.24 μg/mL)>타임(71.97 μg/mL)>딜(69.37 μg/mL)>차이브(33.09 μg/mL) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 확인되어 파슬리 추출물이 가장 높은 함량이 확인되었다.
나. DPPH 라디컬 소거능
항산화 물질의 가장 특징적인 기작은 유리기와 반응하는 것으로 free radical 소거 작용은 활성라디칼에 전자를 공여하여 항산화 효과나 인체에서 노화를 억제하는 척도로 사용되고 있다(Lee et al., 2016). DPPH 방법에 의한 free radical 소거능은 안정한 활성산소종으로 항산화 물질의 항산화력을 검증하는데 널리 사용되고 있다(Choi & Moon, 2017).
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 DPPH radical 소거 활성을 측정한 결과 Figure 1과 같으며, 500 μg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(92.36%)>파슬리(91.18%)>타임(90.0%)>차이브(85.0%)>딜(78.31%) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 소거능이 확인되었다. 대조군인 Vit C는 94.50%, BHT는 81.28%의 효능이 확인되어 Vit C 보다는 낮지만 로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임 에탄올 추출물은 BHT 보다 높은 소거능이 확인되었다.

DPPH free radical scavenging activity of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts.
DPPH radical scavenging assays were conducted to investigate the anti-oxidant effects of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts at varying concentration of 15.7, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 μg/mL. Vit C, ascorbic acid; BHT, butylated hydroxytoluene group.
다. ABTS 라디컬 소거능
ABTS 라디칼 소거능은 DPPH방법과 함께 항산화 활성을 스크리닝하는데 가장 기초가 되는 실험으로 친수성 및 소수성 화합물의 항산화력 측정이 가능하고, 비교적 높은 734 nm의 파장에서 최대의 흡광도를 가져 추출물 고유의 색소에 의한 영향이 최소한으로 작용하여 항산화력을 측정할 수 있다고 보고되고 있다(Lee & Moon, 2019).
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 ABTS radical 소거 활성을 측정한 결과 Figure 2와 같으며, 500 μg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(95.21%)>파슬리(94.32%)>타임(92.14%)> 차이브(88.90%)>딜(82.31%) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 소거능이 확인되었다.

Measurements of ABTS radical scavenging activity of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts.
ABTS radical scavenging activity assays were conducted to investigate the anti-oxidant effects of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts at varying concentration of 15.7, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 μg/mL. Vit C, ascorbic acid; BHT, butylated hydroxytoluene.
대조군인 Vit C는 95.22%, BHT는 85.13%의 효능이 확인되어 로즈마리 에탄올 추출물 Vit C와 유사한 소거능이 확인되었으며, 딜 에탄올 추출물을 제외하고 BHT 보다 높은 소거능이 확인되었다.
라. SOD 유사활성
SOD는 생리활성을 나타내는 항산화 효소 중 하나로, 과산화수소는 SOD에 의해 생성되어 peroxidase 또는 catalase에 의해 물과 산소로 전환되어 항산화 역할을 하고, 생체를 보호하는 기능을 한다(Um, 2020). SOD 활성을 가진 소재는 함영증 제재나 피부노화 방지를 위한 화장품 첨가제로 사용될 수 있다(Song & Lee, 2015). 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 SOD 유사활성 활성을 측정한 결과 Figure 3과 같으며, 500 μg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(84.17%)>파슬리(83.18%)>타임(80.87%)>차이브(72.39%)>딜(66.31) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 확인되었다.
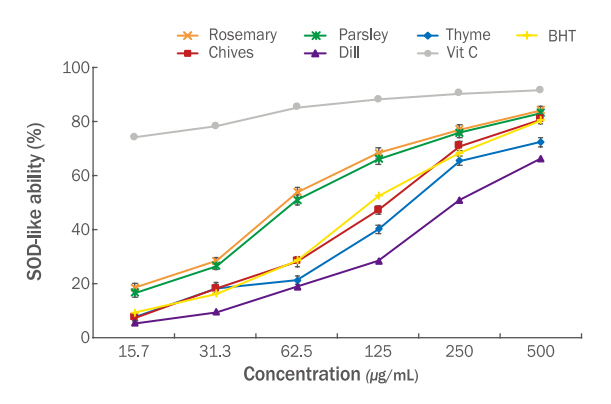
SOD-like activity of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts.
SOD-like activity assays were conducted to investigate the antioxidant effects of rosemary, parsley, chives, thyme and dill ethanol extracts at concentration of 15.7, 31.3, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 μg/mL. Vit C, ascorbic acid; BHT, butylated hydroxytoluene.
대조군인 Vit C는 91.52%, BHT는 80.41%의 효능이 확인되어 로즈마리, 파슬리, 타임 에탄올 추출물은 BHT 보다 높은 유사활성이 확인되었다.
2. 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜) 에탄올 추출물의 항균효과
가. Staphylococcus epidermidis에 대한 항균효과
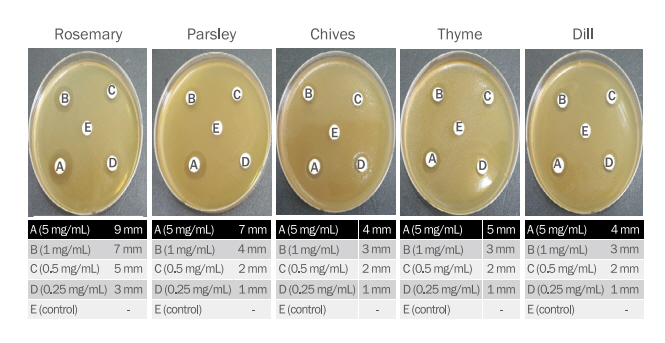
S. epidermidis는 피부나 환경 중에 존재하고 있는 병원성 세균으로, 주로 염증을 통해서 고름형성, 피부발진 등의 증상으로 감염이 나타난다(Yang & Jang 2019). 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의S. epidermidis에 대한 항균효과는 Figure 4와 같이 5 mg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(7 mm)=파슬리(7 mm)=타임(7 mm)>차이브(2 mm)=딜(2 mm) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 확인되었으며, 대조군은 clear zone이 확인되지 않았다.
나. Propionibacterium acnes에 대한 항균효과
여드름은 P. acnes에 의해 피부 모낭 주변의 피지선에서 유발되는 염증성 질환으로 항균효과를 측정결과 Figure 5와 같이 5 mg/mL 농도에서 로즈마리(9 mm)>파슬리(7 mm)>타임(5 mm)>차이브(4 mm)=딜(4 mm) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 확인되었으며, 대조군은 clear zone이 확인되지 않았다.
다. Corynebacterium xerosis에 대한 항균효과
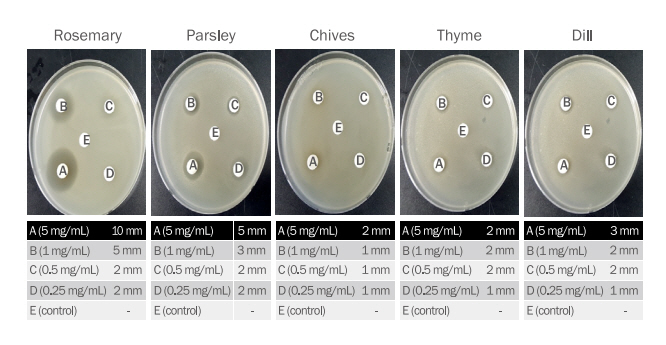
액취는 아포크린 한선 질환으로 피부에서 악취가 나는 악취성 발한이며, 주로 액와에서 발생된다. 액취의 특유한 냄새는 겨드랑이 등 특정부위에 분포되어 있는 아포크린 한선에 있는 세균의 일종인 피부상재균에 의해 분해되거나 또는 자가 산화되어 불쾌한 냄새의 지방산을 생산하기 때문에 발생한다(Roh et al., 2009). C. xerosis에 대한 항균효과를 측정한 결과 Figure 6과 같이 5 mg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(10 mm)>파슬리(5 mm)>딜(3 mm)>타임(2 mm)=차이브(2 mm) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 항균효과가 확인되었으며, 대조군은 clear zone이 확인되지 않았다.
라. Malassezia furfur에 대한 항균 효과
M. furfur는 두피에 존재하는 균의 한 종류로서 생리적 요인, 환경적 요인에 의해 과산화지질과 지방산 등이 생성되면 두피에 있는 표피세포를 증가시켜 비듬, 지루성 피부염, 탈모 등의 피부질환을 유발하는 것으로 알려져 있다(Jang et al., 2018; Lee & Kim, 2020b).
M. furfur에 대한 항균효과를 측정한 결과 Figure 7과 같이 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물 5 mg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(9 mm)>파슬리(7 mm)>딜(6 mm)>차이브(3 mm)>타임(3 mm) 에탄올 추추물 순으로 항균효과가 확인되었으며, 대조군은 clear zone이 확인되지 않았다.
마. Trichophyton mentagrophytes에 대한 항균효과
T. mentagrophytes는 표재성 진균증의 대표적인 원인균으로써 두피, 피부 및 손발톱을 통해 감염되어 무좀을 유발한다. T. mentagrophytes에 대한 항균효과를 측정한 결과 Figure 8과 5 mg/mL의 농도에서 로즈마리(8 mm)>파슬리(5 mm)=차이브(5 mm)=딜(5 mm)=타임(5 mm) 에탄올 추출물 순으로 항균효과가 확인되었으며, 대조군은 clear zone이 확인되지 않았다.
Conclusion
본 연구는 5종의 허브(로즈마리, 파슬리, 차이브, 타임, 딜) 에탄올 추출물의 항산화효과, 피부질환 원인균에 대한 항균효과를 측정한 결과 다음과 같다.
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 항산화효과를 측정한 결과 1 mg/mL에 포함되어 있는 총 폴리페놀 함량은 로즈마리>파슬리>타일>차이브>딜 순으로 확인되었으며, 총 플라보노이드는 파슬리>로즈마리>타임>딜>차이브 순으로 함량이 확인되었다.
DPPH 라디컬 소거능은 로즈마리>파슬리>타임>차이브>딜순으로 소거능이 확인되었으며, ABTS 라디컬 소거능은 로즈마리>파슬리>타임>차이브>딜 순으로 소거능이 확인 되었다. SOD 유사활성은 로즈마리>파슬리>타임 >차이브>딜 순으로 확인되었다.
5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물의 항균효과를 측정한 결과 5 mg/mL의 농도에서 S. epidermidis에 대한 항균효과는 파슬리=로즈마리=타임>차이브=딜 순으로 확인 되었으며, P. acnes에 대한 항균효과 로즈마리>파슬리>딜>타임=차이브 순으로 확인되었다. C. xerosis에 대한 항균효과는 로즈마>파슬리>딜>타임>차이브 순으로 확인되었다. M. furfur에 대한 항균효과는 로즈마리>파슬리>딜>차이브>타임 순으로 확인 되었다. T. mentagrophytes에 대한 항균효과는 로즈마리>파슬리>차이브>딜>타임 순으로 확인되었다.
이상의 결과 5종의 허브 에탄올 추출물은 항산화 및 항균효과가 확인되어 천연항균제 및 향장품 소재로서의 가능성이 확인되었다.
Notes
Author's contribution
RJP and MJR contributed equally to this work. RJP and MJR designed all experimental investigations and developed manufacturing process of five extracts of rosemary, parsley, thyme, chive, and dill. Bioactivity experiments were performed together by RJP and MJR. MJR oversaw the project and contributed to all aspects of analysis and experimental design. MJR wrote the manuscript with the help of RJP.
Author details
Rang Ju Park (Graduate Student), Department of Cosmetology Science, Nambu University, 23 advanced Jungang-ro, Gwangsan-gu, Gwangju 62271, Korea; Min Jeong Ryu (Professor), Department of Cosmetology Science, Nambu University, 23 advanced Jungang-ro, Gwangsan-gu, Gwangju 62271, Korea.